Search Results for: organic matter
Organic matter
Definition noun Any of the carbon-based compounds found in nature Supplement Organic matter pertains to any of the... Read More
Decomposer
Decomposer Definition The organisms that carry out the process of decay or breakdown of the dead organism are known as... Read More
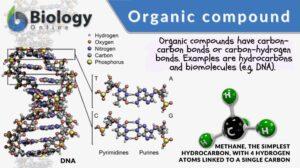
Organic compound
Organic Compound Definition An organic compound is a compound that, in general, contains carbon covalently bound to other... Read More
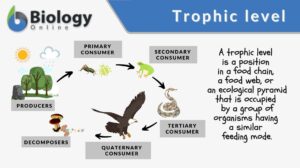
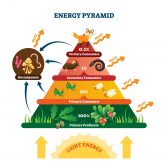
Trophic level
In ecology, a trophic level pertains to a position in a food chain or ecological pyramid occupied by a group of organisms... Read More
Heterotroph
Heterotroph Definition What is a heterotroph? Does a heterotroph make its own food? In biology and ecology, a heterotroph... Read More
Primary productivity
Planet Earth is home to different types of life forms ranging from microscopic bacteria to giant whales and elephants. To... Read More
Recalcitrant
Several words of the English language find wide usage in subjects as diverse as literature, science, social science,... Read More
Biotic factor
Biotic Factor Definition A biotic factor is the living component in an ecosystem. The term "biotic" means "of or related... Read More
Net primary productivity
In order to keep the biosphere running, different organisms play different roles and functions. Some help in oxygen... Read More
Global Carbon Cycling on a Heterogeneous Seafloor
Carbon, nitrogen and oxygen are the fundamental elements of life on Earth. Global carbon varies in amount and its... Read More
Light-dependent reaction
Many organisms, such as green plants, convert light energy into chemical energy through the mechanism of photosynthesis. In... Read More
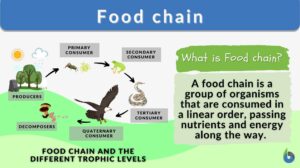
Food chain
Everything is a cycle in life. The way organisms consume their food also follows a cycle. This is usually described as the... Read More
Chemoheterotroph
Definition noun, plural: chemoheterotrophs An organism deriving energy by ingesting intermediates or building blocks that it... Read More
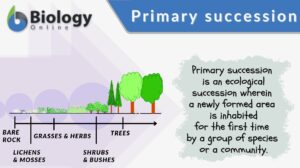
Primary succession
Primary Succession Definition Primary succession is an ecological succession where a newly formed area is inhabited for the... Read More
Freshwater Community Energy Relationships – Producers & Consumers
The previous tutorial on producers and consumers noted the reliance that organisms have on one another to obtain energy to... Read More
Primary consumer
Definition noun, plural: primary consumers Any organism that consumes or feeds on autotrophs Supplement A food chain is... Read More
Detritivore
Definition noun, plural: detritivores An organism that feeds on detritus or organic waste Supplement A detritivore pertains... Read More
Unicellular
Unicellular organisms are organisms consisting of one cell only that performs all vital functions including metabolism,... Read More
Phenol coefficient
Chemical disinfectants are categorized based on the power of their disinfection for microbes and viruses. Strong... Read More
Carbon dioxide
Carbon Dioxide Definition noun, car·bon di·ox·ide, /daɪˈɒksaɪd/ (biochemistry) An inorganic compound, with the... Read More
Eubacteria
Eubacteria are prokaryotic microorganisms consisting of a single cell lacking a nucleus and containing DNA is a single... Read More
Tertiary consumer
Definition noun, plural: tertiary consumers Any organism that consumes or feeds largely on primary and secondary... Read More
Running Water Freshwater Community Factors
This tutorial continues from the previous one, which introduced lotic (running water) communities. Here, some of the... Read More
Great Oxygenation Event
Great Oxygenation Event Definition The Great Oxygenation Event is defined as the surge of dioxygen (O2) levels in the... Read More
Calvin cycle
Calvin Cycle Definition The Calvin cycle, also known as the Calvin Benson cycle or the dark reactions, is a series of... Read More
Photoheterotroph
Definition noun, plural: photoheterotrophs An organism that depends on light for most of its energy and principally on... Read More